Back Pain Treatment
The care plan from our Weston Medical Health Center team works to restore function to the spinal joints to relieve the muscles from the splinting cycle. The most effective treatment for this is Spinal Decompression Therapy. This therapy relieves pressure on the disk to allow the body to heal naturally. Once the nervous system and muscles calm down your pain will begin to subside. Far too many sufferers of back pain are quick to accept the use of medications and/or surgery as the only options, without considering other less invasive and less traumatic back pain treatments. This approach to back pain and proper care from our Florida medical team has created life changing results for hundreds, who now live free of back pain yet never having to undergo back surgery.
At Weston Medical Health Center our mission is simple to get you out of pain as quick as possible. Then provide therapeutic care to prevent the pain from returning by incorporating all the amenities available. As one of the leading pain management medical clinics in Florida we are able to provide care from medical doctors, chiropractors, and physical therapist from one location. This gives our patients the benefit of multidisciplinary care plans with a whole body approach to provide lasting pain relief.

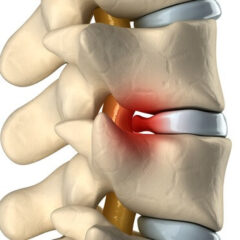

Causes of Back Pain
Back Pain affects around 80% of Americans at one point in their life. Back pain can be caused by hundreds of potential factors, spinal and nerve damage from accidents can bring about strains and injuries with chronic back pain symptoms. Misalignment, caused from weight gain, poor posture, repetitive movement, and bone deterioration can also lead to chronic back pain. Once the spinal tissues are irritated, the muscles begin a splinting process and lock down the spinal joints. This splinting creates spinal joint dysfunction, swelling and inflammation.
About Lower Back Pain
As people age, bone strength and muscle elasticity and tone tend to decrease. The spinal discs begin to lose fluid and flexibility, which decreases their ability to cushion the vertebrae. Lower back pain can occur when, for example, someone lifts something too heavy or over stretches, causing a sprain, strain, or spasm in one of the muscles or ligaments in the back. If the spine becomes overly strained or compressed, a disc may rupture or bulge outward. This rupture may put pressure on one of the more than 50 nerves rooted to the spinal cord that control body movements and transmit signals from the body to the brain. When these nerve roots become compressed or irritated, lower back pain results. Lower back pain may reflect nerve or muscle irritation or bone lesions.
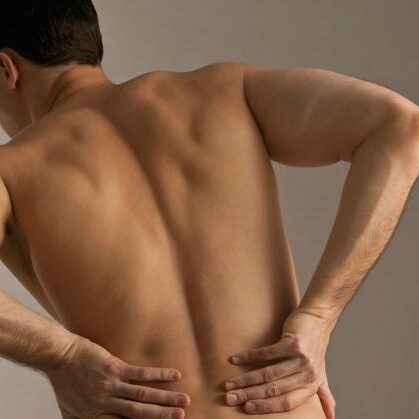
Most lower back pain follows injury or trauma to the back, but pain may also be caused by degenerative conditions such as arthritis or disc disease, osteoporosis or other bone diseases, viral infections, irritation to joints and discs, or congenital abnormalities in the spine.
Obesity, smoking, weight gain during pregnancy, stress, poor physical condition, posture inappropriate for the activity being performed, and poor sleeping position also may contribute to lower back pain.
Additionally, scar tissue created when the injured back heals itself does not have the strength or flexibility of normal tissue. Buildup of scar tissue from repeated injuries eventually weakens the back and can lead to more serious injury.
Occasionally, lower back pain may indicate a more serious medical problem. Pain accompanied by fever or loss of bowel or bladder control, pain when coughing, and progressive weakness in the legs may indicate a pinched nerve or other serious condition. People with diabetes may have severe lower back pain or pain radiating down the leg related to neuropathy. People with these symptoms should contact a doctor immediately to help prevent permanent damage.